分布式文件系统-QFS
Quantcast File System (QFS) 是一个高性能、容错、分布式的文件系统,其开发是用于支持 MapReduce 处理或者需要顺序读写大文件的应用。采用C/C++开发并在Apache协议下授权使用。
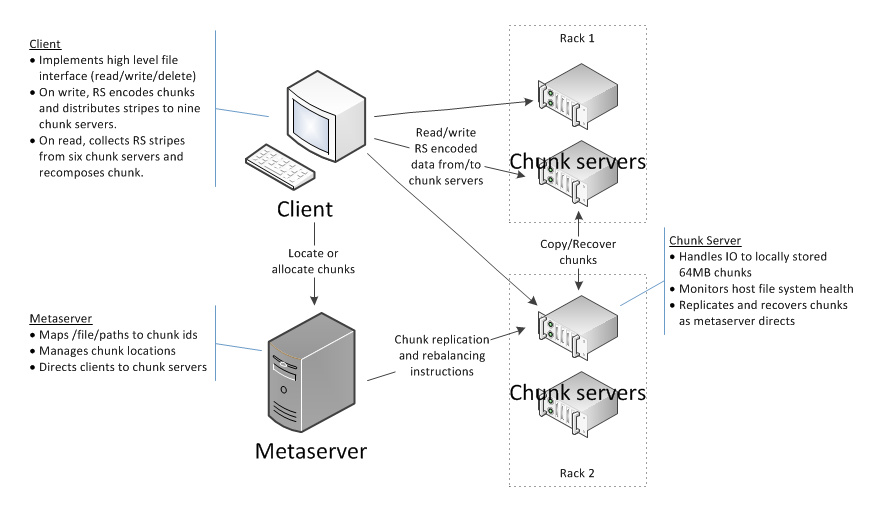
Quantcast File System (QFS) is a high-performance, fault-tolerant, distributed file system developed to support MapReduce processing, or other applications reading and writing large files sequentially.
QFS consists of 3 components:
Metaserver
A central metadata server that manages the file system's directory structure and mappings of files to physical storage.
Chunk Server
The distributed component of the distributed file system. There's one chunk server for each machine that will store data, and it manages I/O to all the disks on that machine (via, for example, XFS or ext3 on Linux).
Client Library
Library that provides the file system API to allow applications to interface with QFS. To integrate applications to use QFS, applications will need to be modified and relinked with the QFS client library.
QFS is implemented in C++ using standard system components such as TCP sockets, STL, and Boost libraries. The server components have been used in production on 64-bit x86 architectures running Linux CentOS 5 and 6, and the client library has been tested on CentOS 5 and 6, OSX 10.X, Cygwin, and Debian/Ubuntu.
Features
Incremental Scalability
Chunk Servers can be added to the system in an incremental fashion. When a chunk server is added, it establishes a connection to the metaserver and becomes part of the system. No metaserver restarts are needed.
Balancing
During data placement, the metaserver tries to keep the data balanced across all nodes in the system.
Rebalancing
The metaserver will rebalance data among the nodes in the system when the server detects that some nodes are under-utilized (i.e., < 20% of the chunk server's exported space is used) and other nodes are over-utilized (i.e., > 80% of a chunk server's exported space is used).
Fault Tolerance
Tolerating missing data is the central design challenge for a distributed file system. QFS supports both per-chunk replication (storing multiple copies of each chunk) and Reed-Solomon 6+3 encoding (storing stripes of parity data that can rebuild chunks without storing all of the original data).
Fine-tunable Replication, Striping, Recovery Mode
The degree of replication, striping, and recovery mode can be configured on a per-file basis.
Re-replication
Whenever the degree of replication for a file drops below the configured amount (for example, due to an extended chunk server outage), the metaserver automatically forces the block to be re-replicated on the remaining chunk servers. Re-replication is done in the background without overwhelming the system.
Data Integrity
To handle disk corruptions within data blocks, data blocks are checksummed. Whenever a chunk is read, checksum verification is performed; whenever there is a checksum mismatch, re-replication is used to recover the corrupted chunk.
Client Side Metadata Caching
The QFS client library caches directory related metadata to avoid repeated server lookups for pathname translation. The metadata entries expire from the cache after 30 secs.
File Writes
The QFS client library employs a write-back cache. Also, whenever the cache is full, the client will flush the data to the chunk servers. Applications can choose to flush data to the chunk servers via a sync() call.
Leases
The QFS client library uses caching to improve performance. Leases are used to support cache consistency.
Versioning
Chunks are versioned to permit detection of "stale" chunks. For instance, consider the following scenario:
Let chunk servers s1, s2, and s3 store version v of chunk c.
Suppose that s1 fails, and when s1 is down a client writes to c.
The write will succeed at s2 and s3, and the version # will change to v'.
When s1 is restarted, it notifies the metaserver of all the versions of all chunks it has.
When the metaserver sees that s1 has version v of chunk c, but the latest is v', the metaserver will notify s1 that its copy of c is stale.
s1 will delete c.
Client Side Fail-over
The client library is resilient to chunk server failures. During reads, if the client library determines that the chunk server it was communicating with is unreachable, the client library will fail over to another chunk server and continue the read. This failover is transparent to the application.
Language Support
The QFS client library can be accessed from C++ and Java. A experimental Python access module is also available.
Tools
The command line tool for accessing QFS gets installed as .../bin/tools/qfs. It is meant as a drop in for hadoop fs. Unlike hadoop fs, there is no JVM loading when you invoke this tool, which brings the time to stat a file from 700 milliseconds to below 10 milliseconds in our tests. Additional tools for loading/unloading data into QFS, as well as tools to monitor the chunk servers and metaserver are also provided.
FUSE support on Linux
By mounting QFS via FUSE, this support allows existing linux utilities (such as ls) to interface with QFS.
Unix style permissions support
最新版本:1.0
项目主页:http://quantcast.github.io/qfs/

Quantcast File System (QFS) is a high-performance, fault-tolerant, distributed file system developed to support MapReduce processing, or other applications reading and writing large files sequentially.
QFS consists of 3 components:
Metaserver
A central metadata server that manages the file system's directory structure and mappings of files to physical storage.
Chunk Server
The distributed component of the distributed file system. There's one chunk server for each machine that will store data, and it manages I/O to all the disks on that machine (via, for example, XFS or ext3 on Linux).
Client Library
Library that provides the file system API to allow applications to interface with QFS. To integrate applications to use QFS, applications will need to be modified and relinked with the QFS client library.
QFS is implemented in C++ using standard system components such as TCP sockets, STL, and Boost libraries. The server components have been used in production on 64-bit x86 architectures running Linux CentOS 5 and 6, and the client library has been tested on CentOS 5 and 6, OSX 10.X, Cygwin, and Debian/Ubuntu.
Features
Incremental Scalability
Chunk Servers can be added to the system in an incremental fashion. When a chunk server is added, it establishes a connection to the metaserver and becomes part of the system. No metaserver restarts are needed.
Balancing
During data placement, the metaserver tries to keep the data balanced across all nodes in the system.
Rebalancing
The metaserver will rebalance data among the nodes in the system when the server detects that some nodes are under-utilized (i.e., < 20% of the chunk server's exported space is used) and other nodes are over-utilized (i.e., > 80% of a chunk server's exported space is used).
Fault Tolerance
Tolerating missing data is the central design challenge for a distributed file system. QFS supports both per-chunk replication (storing multiple copies of each chunk) and Reed-Solomon 6+3 encoding (storing stripes of parity data that can rebuild chunks without storing all of the original data).
Fine-tunable Replication, Striping, Recovery Mode
The degree of replication, striping, and recovery mode can be configured on a per-file basis.
Re-replication
Whenever the degree of replication for a file drops below the configured amount (for example, due to an extended chunk server outage), the metaserver automatically forces the block to be re-replicated on the remaining chunk servers. Re-replication is done in the background without overwhelming the system.
Data Integrity
To handle disk corruptions within data blocks, data blocks are checksummed. Whenever a chunk is read, checksum verification is performed; whenever there is a checksum mismatch, re-replication is used to recover the corrupted chunk.
Client Side Metadata Caching
The QFS client library caches directory related metadata to avoid repeated server lookups for pathname translation. The metadata entries expire from the cache after 30 secs.
File Writes
The QFS client library employs a write-back cache. Also, whenever the cache is full, the client will flush the data to the chunk servers. Applications can choose to flush data to the chunk servers via a sync() call.
Leases
The QFS client library uses caching to improve performance. Leases are used to support cache consistency.
Versioning
Chunks are versioned to permit detection of "stale" chunks. For instance, consider the following scenario:
Let chunk servers s1, s2, and s3 store version v of chunk c.
Suppose that s1 fails, and when s1 is down a client writes to c.
The write will succeed at s2 and s3, and the version # will change to v'.
When s1 is restarted, it notifies the metaserver of all the versions of all chunks it has.
When the metaserver sees that s1 has version v of chunk c, but the latest is v', the metaserver will notify s1 that its copy of c is stale.
s1 will delete c.
Client Side Fail-over
The client library is resilient to chunk server failures. During reads, if the client library determines that the chunk server it was communicating with is unreachable, the client library will fail over to another chunk server and continue the read. This failover is transparent to the application.
Language Support
The QFS client library can be accessed from C++ and Java. A experimental Python access module is also available.
Tools
The command line tool for accessing QFS gets installed as .../bin/tools/qfs. It is meant as a drop in for hadoop fs. Unlike hadoop fs, there is no JVM loading when you invoke this tool, which brings the time to stat a file from 700 milliseconds to below 10 milliseconds in our tests. Additional tools for loading/unloading data into QFS, as well as tools to monitor the chunk servers and metaserver are also provided.
FUSE support on Linux
By mounting QFS via FUSE, this support allows existing linux utilities (such as ls) to interface with QFS.
Unix style permissions support
最新版本:1.0
项目主页:http://quantcast.github.io/qfs/
