PPTP、L2TP、IPSec和SSL VPN的区别
VPN (虚拟专用网)发展至今已经不在是一个单纯的经过加密的访问隧道了,它已经融合了访问控制、传输管理、加密、路由选择、可用性管理等多种功能,并在全球的 信息安全体系中发挥着重要的作用。也在网络上,有关各种VPN协议优缺点的比较是仁者见仁,智者见智,很多技术人员由于出于使用目的考虑,包括访问控制、 安全和用户简单易用,灵活扩展等各方面,权衡利弊,难以取舍;尤其在VOIP语音环境中,网络安全显得尤为重要,因此现在越来越多的网络电话和语音网关支 持VPN协议。
一、PPTP
点对点隧道协议 (PPTP) 是由包括微软和3Com等公司组成的PPTP论坛开发的一种点对点隧道协,基于拨号使用的PPP协议使用PAP或CHAP之类的加密算法,或者使用 Microsoft的点对点加密算法MPPE。其通过跨越基于 TCP/IP 的数据网络创建 VPN 实现了从远程客户端到专用企业服务器之间数据的安全传输。
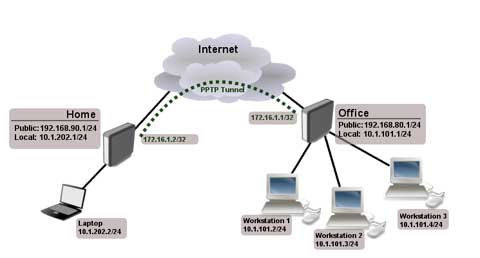
PPTP 支持通过公共网络(例如 Internet)建立按需的、多协议的、虚拟专用网络。PPTP 允许加密 IP 通讯,然后在要跨越公司 IP 网络或公共 IP 网络(如 Internet)发送的 IP 头中对其进行封装。
PPTP协议是点对点隧道协议,其将控制包与数据包分开,控制包采用TCP控制。PPTP使用TCP协议,适合在没有防火墙限制的网络中使用。
二、L2TP
第 2 层隧道协议 (L2TP) 是IETF基于L2F (Cisco的第二层转发协议)开发的PPTP的后续版本。是一种工业标准 Internet 隧道协议,其可以为跨越面向数据包的媒体发送点到点协议(PPP)框架提供封装。PPTP和L2TP都使用PPP协议对数据进行封装,然后添加附加包头用于数据在互联网络上的传输。PPTP只能在两端点间建立单一隧道。
L2TP支持在两端点间使用多隧道,用户可以针对不同的服务质量创建不同的隧道。L2TP可以提供隧道验证,而PPTP则不支持隧道验证。但是当L2TP 或PPTP与IPSEC共同使用时,可以由IPSEC提供隧道验证,不需要在第2层协议上验证隧道使用L2TP。PPTP要求互联网络为IP网络。L2TP只要求隧道媒介提供面向数据包的点对点的连接,L2TP可以在IP(使用UDP),桢中继永久虚拟电路 (PVCs),X.25虚拟电路(VCs)或ATM VCs网络上使用。
L2TP是国际标准隧道协议,它结合了PPTP协议以及第二层转发L2F协议的优点,能以隧道方式使PPP包通过各种网络协议,包括ATM、SONET和帧中继。但是L2TP没有任何加密措施,更多是和IPSec协议结合使用,提供隧道验证。
L2TP使用UDP协议,一般可以穿透防火墙,适合在有防火墙限制、局域网用户,如公司、网吧、学校等场合使用。PPTP和L2TP二个连接类型在性能上差别不大,如果使用PPTP不正常,那就更换为L2TP。
三、IPSec
IPSec隧道模式隧道是封装、路由与解封装的整个过程。隧道将原始数据包隐藏(或封装)在新的数据包内部。该新的数据包可能会有新的寻址与路由信息,从而使其能够通过网络传输。隧道与数据保密性结合使用时,在网络上窃听通讯的人将无法获取原始数据包数据(以及原始的源和目标)。封装的数据包到达目的地后,会删除封 装,原始数据包头用于将数据包路由到最终目的地。
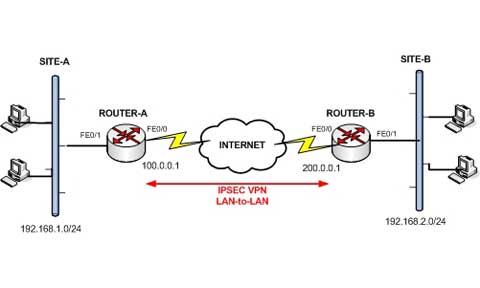
隧道本身是封装数据经过的逻辑数据路径,对原始的源和目的端,隧道是不可见的,而只能看到网络路径中的点对点连接。连接双方并不关心隧道起点和终点之间的任何路由器、交换机、代理服务器或其他安全网关。将隧道和数据保密性结合使用时,可用于提供VPN。
封装的数据包在网络中的隧道内部传输。在此示例中,该网络是 Internet。网关可以是外部 Internet与专用网络间的周界网关。周界网关可以是路由器、防火墙、代理服务器或其他安全网关。另外,在专用网络内部可使用两个网关来保护网络中不信任的通讯。
当以隧道模式使用 IPSec 时,其只为 IP 通讯提供封装。使用 IPSec 隧道模式主要是为了与其他不支持 IPSec 上的 L2TP 或 PPTP VPN 隧道技术的路由器、网关或终端系统之间的相互操作。
四、SSL VPN
SSL协议提供了数据私密性、端点验证、信息完整性等特性。SSL协议由许多子协议组成,其中两个主要的子协议是握手协议和记录协议。握手协议允许 服务器和客户端在应用协议传输第一个数据字节以前,彼此确认,协商一种加密算法和密码钥匙。在数据传输期间,记录协议利用握手协议生成的密钥加密和解密后 来交换的数据。
SSL独立于应用,因此任何一个应用程序都可以享受它的安全性而不必理会执行细节。SSL置身于网络结构体系的 传输层和应用层之间。此外,SSL本身就被几乎所有的Web浏览器支持。这意味着客户端不需要为了支持SSL连接安装额外的软件。这两个特征就是SSL能 应用于VPN的关键点。
典型的SSL VPN应用如OpenVPN,是一个比较好的开源软件。PPTP主要为那些经常外出移动或家庭办公的用户考虑;而OpenVPN主要是针对企业异地两地总分公司之间的VPN不间断按需连接,例如ERP在企业中的应用。
五、OpenVPN产品特点
OpenVPN 允许参与建立VPN的单点使用预设的私钥,第三方证书,或者用户名/密码来进行身份验证。它大量使用了OpenSSL加密库,以及SSLv3/TLSv1 协议。OpenVPN能在Linux、xBSD、Mac OS X与Windows 2000/XP上运行。它并不是一个基于Web的VPN软件,也不与IPsec及其他VPN软件包兼容。
隧道加密
OpenVPN使用OpenSSL库加密数据与控制信息:它使用了OpesSSL的加密以及验证功能,意味着,它能够使用任何OpenSSL支持的算法。它提供了可选的数据包HMAC功能以提高连接的安全性。此外,OpenSSL的硬件加速也能提高它的性能。
OpenVPN提供了多种身份验证方式,用以确认参与连接双方的身份,包括:预享私钥,第三方证书以及用户名/密码组合。预享密钥最为简单,但同时 它只能用于建立点对点的VPN;基于PKI的第三方证书提供了最完善的功能,但是需要额外的精力去维护一个PKI证书体系。OpenVPN2.0后引入了 用户名/口令组合的身份验证方式,它可以省略客户端证书,但是仍有一份服务器证书需要被用作加密.
OpenVPN所有的通信都基于一个单一的IP端口,默认且推荐使用UDP协议通讯,同时TCP也被支持。OpenVPN连接能通过大多数的代理服务器,并且能够在NAT的环境中很好地工作。服务端具有向客户端“推送”某些网络配置信息的功能,这些信息包括:IP地址、路由设置等。OpenVPN提供了两种虚拟网络接口:通用Tun/Tap驱动,通过它们,可以建立三层IP隧道,或者虚拟二层以太网,后者可以传送任何类型的二层以太网络数据。传送的 数据可通过LZO算法压缩。IANA(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority)指定给OpenVPN的官方端口为1194。OpenVPN 2.0以后版本每个进程可以同时管理数个并发的隧道。
OpenVPN使用通用网络协议(TCP与UDP)的特点使它成为IPsec等协议的理想替代,尤其是在ISP(Internet service provider)过滤某些特定VPN协议的情况下。在选择协议时候,需要注意2个加密隧道之间的网络状况,如有高延迟或者丢包较多的情况下,请选择TCP协议作为底层协议,UDP协议由于存在无连接和重传机制,导致要隧道上层的协议进行重传,效率非常低下。
OpenVPN与生俱来便具备了许多安全特性:它在用户空间运行,无须对内核及网络协议栈作修改;初始完毕后以chroot方式运行,放弃root权限;使用mlockall以防止敏感数据交换到磁盘。
OpenVPN通过PKCS#11支持硬件加密标识,如智能卡。
OpenVPN是一个基于SSL加密的纯应用层VPN协议,是SSL VPN的一种,支持UDP与TCP两种方式(说明:UDP和TCP是2种通讯协议,这里通常UDP的效率会比较高,速度也相对较快。所以尽量使用UDP连接方式,实在UDP没法使用的时候,再使用TCP连接方式)。
由于其运行在纯应用层,避免了PPTP和L2TP在某些NAT设备后面不被支持的情况,并且可以绕过一些网络的封锁(通俗点讲,基本上能上网的地方就能用OpenVPN)。OpenVPN客户端软件可以很方便地配合路由表,实现不同线路(如国内和国外)的路由选择,实现一部分IP走VPN,另一部分IP走原网络。
PPTP和L2TP的区别
PPTP和L2TP只是VPN的两种连接方式,只是方式不同,因为每个人的网络环境的差异,需要用适合自己的连接方式,一般首选是PPTP,也有部分使用PPTP不稳定或者无法连接的用户,换L2TP方式连接即可得到很好的解决。
PPTP
点对点点对点隧道协议(PPTP),由微软开发的,与其他技术公司一起,是最广泛支持的Windows客户端的VPN之间的方法。PPTP是一个扩展的互联网标准的点对点点对点协议(PPP),链路层协议,用于在串行链路上传输的IP数据包。PPTP使用相同类型的身份验证的PPP(PAP,SPAP,CHAP,MS-CHAP v.1/v.2和EAP)。
PPTP建立隧道,但不提供加密,PPTP使用微软点对点加密(MPPE)协议来创建一个安全的VPN加密链接。PPTP具有相对较低的开销,这使得它比其他一些VPN方法部署更快。
如何工作:PPTP隧道被实例化的对等通信的TCP端口1723。这个TCP连接,然后用第二GRE(通用路由封装)隧道到同一个发起和管理。
端口/协议: 1723 TCP协议GRE
用户认证协议 EAP-TLS或MS-CHAP v2的
MPPE(微软点对点点对点加密)加密方法:
加密强度: MPPE 40-128位
L2TP
第2层隧道协议(L2TP),思科与微软之间的合作开发的 PPTP的功能结合起来,与思科的专有第2层转发协议(L2F)。
L2TP(第二层隧道协议)支持non-TCP/IP客户和协议(如帧中继,ATM和SONET)。
L2TP不提供任何加密orconfidentiality,本身它依赖于一种加密协议,它通过在隧道内提供保密性。如今L2TP连接 不谈判PPP加密通过使用微软点对点加密(MPPE) 。相反,加密是通过使用Internet协议安全(IPSec)的封装安全负载(ESP)头和尾。同样重要的是要注意,IPsec是比PPTP消耗更多的资源,因此高于PPTP与L2TP溶液的开销。
端口: 1701 UDP
用户认证协议 EAP-TLS或MS-CHAP v2的
*除了提供计算机级身份验证,IPSec提供终端到终端的发送和接收节点之间传递数据的加密。
安全加密:
加密强度: 高级加密标准(AES)256,AES 192,AES 128和3DES加密算法。
L2TP/IPSec和PPTP类似在以下方面:
提供了一个逻辑的传输机制来发送PPP有效载荷。
提供隧道或PPP有效载荷基于任何协议的封装,使得可以通过IP网络发送。
依靠PPP连接过程执行用户认证和协议配置。
有关PPTP的一些特点:
+ PPTP 易于部署
PPTP使用TCP,可靠的解决方案,允许重传丢失的数据包
+支持PPTP
- PPTP的安全性较低,MPPE(最多128位)
-数据加密后开始PPP连接过程(因此,PPP认证)完成
- PPTP连接只需要通过基于PPP的认证协议的用户级身份验证
一些事实over IPSec的L2TP():
+ L2TP/IPSec的数据加密之前就 已经开始PPP连接过程
+ L2TP/IPSec的连接使用三个56位密钥的AES(256位)或DESUup)
+ L2TP/IPSec的连接需要通过计算机级别的认证证书和用户级认证通过PPP认证协议,提供了更强的身份验证
+ L2TP使用UDP。它是一个速度更快,但不太可靠,因为它并没有重新传输丢失的数据包,是常用的实时互联网通信
+ L2TP更多的“防火墙友好”比PPTP -一个关键的优势外联网协议,由于大多数防火墙不支持GRE
- L2TP要求证书签发计算机证书的基础设施
共同点:
PPTP和L2TP都使用PPP协议对数据进行封装,然后添加附加包头用于数据在互联网络上的传输,两个协议非常相似。
不同点:
1、PPTP要求互联网络为IP网络。L2TP只要求隧道媒介提供面向数据包的点对点的连接。L2TP可以在IP(使用UDP),桢中继永久虚拟电路(PVCs),X.25虚拟电路(VCs)或ATM VCs网络上使用。
2、PPTP只能在两端点间建立单一隧道。L2TP支持在两端点间使用多隧道。使用L2TP,用户可以针对不同的服务质量创建不同的隧道。
3、L2TP可以提供包头压缩。当压缩包头时,系统开销(overhead)占用4个字节,而PPTP协议下要占用6个字节。
4、L2TP可以提供隧道验证,而PPTP则不支持隧道验证。但是当L2TP或PPTP与IPSEC共同使用时,可以由IPSEC提供隧道验证,不需要在第2层协议上验证隧道。
使用上的不同:
1、pptp使用简单方便,不需要做额外配置,而l2tp需要共享密钥和修改注册表(对win系列机器讲)。
2、l2tp在穿透方面有时候会比pptp强一些。
3、速度方面两者由于在同一台服务器上,基本没什么差别。
PPTP和L2TP都使用PPP协议对数据进行封装,然后添加附加包头用于数据在互联网络上的传输。尽管两个协议非常相似,但是仍存在以下几方面的不同:
1、PPTP要求互联网络为IP网络。L2TP只要求隧道媒介提供面向数据包的点对点的连接。L2TP可以在IP(使用UDP),桢中继永久虚拟电路(PVCs),X.25虚拟电路(VCs)或ATM VCs网络上使用。
2、PPTP只能在两端点间建立单一隧道。L2TP支持在两端点间使用多隧道。使用L2TP,用户可以针对不同的服务质量创建不同的隧道。
3、L2TP可以提供包头压缩。当压缩包头时,系统开销(overhead)占用4个字节,而PPTP协议下要占用6个字节。
4、L2TP可以提供隧道验证,而PPTP则不支持隧道验证。但是当L2TP或PPTP与IPSEC共同使用时,可以由IPSEC提供隧道验证,不需要在第2层协议上验证隧道。总之,对于一般的使用者来说,L2TP有更强的穿透率,更好的压缩,更好的加密(双层加密),所以如果你在使用PPTP失败的时候可以尝试L2TP。
PPTP、L2TP、OpenVPN三种隧道协议的优缺点对比:
易用性:PPTP > L2TP > OpenVPN
速度:PPTP > OpenVPN UDP > L2TP > OpenVPN TCP
安全性:OpenVPN > L2TP > PPTP
稳定性:OpenVPN > L2TP > PPTP
网络适用性:OpenVPN > PPTP > L2TP
PPTP——最常用,设置最简单,大多数设备都支持
L2TP——支持PPTP的设备基本都支持此种方式,设置略复杂,需要选择L2TP/IPSec PSK方式,且设置预共享密钥PSK
OpenVPN——最稳定,适用于各种网络环境,但需要安装第三方软件和配置文件,较复杂。
PPTP是一个快速、&易于使用协议,具有简单的设置过程。如果您的设备不支持OpenVPN,这是一个不错的选择。
L2TP/IPSec是大多数台式机、手机和平板设备的内建协议。如果您的设备不支持OpenVPN并且安全是重中之重,这是一个不错的选择。IPsec是一项预先安装于大多数台式电脑、手机和平板设备中的协议。我们在指定平台上的IPSec服务支持L2TP和 IKEv2,为您带来快速、安全和可靠的使用体验。
OpenVPN 对于包括Windows, Mac OS X 和 Linux在内的台式机,推荐OpenVPN协议。性能很高——快速,安全,可靠。支持Windows, macOS和Linux等台式电脑操作系统的工业级协议,同时也是一个安全可靠的选择。
WireGuard是最先进、最稳定的VPN协议,它为所有设备提供最快速、最私密和最安全的连接。被认为是VPN协议未来的发展方向。这项灵活的技术由十分简洁的代码架构组成,为您提供最快的速度以及最高级别的隐私性和安全性。
IPSec Vs OpenVPN
user-space (ovpn) vs. kernel-space (IPsec).
opening 1 udp port (ovpn) on the firewall vs. 2-4 ports (isakmp, esp, ah, nat-t) (IPsec).
TLS on steroids (ovpn) vs. IKE (IPsec) for control.
DIY (ovpn) vs. Vendor & IT support (IPsec).
Easy portability (ovpn) vs. difficult portability because of #1 (IPsec).
Ease of compatability with an external peer (ovpn) vs. various vendor implementations of IPsec.
Both can be tough to implement correctly.
Both have quite the learning curve.
Not so much documentation (ovpn) vs. very extensive documentation (IPsec).
Multicast support (ovpn) vs. GRE trickery (IPsec).
L2 support (ovpn) vs. L2TP trickery (IPsec).
Both are as secure (or insecure) as you make them, as they both support more or less the same ciphers & hashes. However, for IPsec, the supported features are limited by the vendor, which means it is slower to adopt emerging encryption tech (ECC, Quantum Encryption, newer stream ciphers) than OpenVPN.
In this chapter, I will be illustrating IPSec Vs OpenVPN | 5 Differences between IPSec and OpenVPN. For this comparison I will be describing the two versions of IPSec, those are the IKEv2/IPSec and the L2TP/IPSec. Let's get started,
1. Installation
Open VPN - Special client software is needed by the OpenVPN for them to be used. They cannot be incorporated into operating system directly. Therefore, custom OpenVPN apps will be provided by the VPN service providers. These custom OpenVPN apps can be used on most of the operating systems and devices.
IKEv2/IPSec - Installation in IKEv2 is made quick and easy. Only the user has to import the configuration files to the servers IKEv2 is being natively Windows, MacOS, IOS and Android devices. Some operating systems also comes with a function known as the ''always on''. This function ensures that there is no data leaks when the traffic is travelling through the VPN tunnel.
L2TP/IPSec - Same as the IKEv2, a L2TP protocol is fast and easy. And also the user only has to import the configuration files to the servers. Furthermore most Windows, MacOS, Android and IOS devices natively support L2TP.
2. Encryption
Open VPN - OpenSSL and the TLS protocol is used by the OpenVPN to provide encryption. Apart from the it uses different algorithms and ciphers. Some of them are Chacha 20, Blowfish, Camellia and AES. AES encryption used by the OpenVPN is of 160bit/256bit.
IKEv2/IPSec - Algorithm used by the IKEv2 is of cryptographic which includes Blowfish, Camellia, 3DES and AES. AES encryption used by the IKEv2 is of 256bit.
L2TP/IPSec - L2TP in default does not offer any kind of encryption. In L2TP the data those which are arriving from the IPSec protocol will be encrypted twice. The AES encryption used by the L2TP is of 256bit.
3. Security
Open VPN - In terms of security, OpenVPN is far most the best protocol. It does have a proper implementation and very less number of vulnerabilities.
IKEv2/IPSec - IKEv2 protocol is considered to be more secure and reliable. In fact it is one of the popular choices for the VPN users. But one the major drawbacks of it is the closed source.
L2TP/IPSec - Same as the IKEv2, the L2TP is also considered to be secure. But it also has a closed source which is its negative side. However since the L2TP is developed by the cisco and microsoft, it is often questioned about trust.
4. Performance
Open VPN - Regardless of using wireless or cellular networks, an OpenVPN can offer stable and reliable performance. The performance offered by the OpenVPN is generally impressive especially when used along with the User Diagram Protocol (UDP). Therefore, whenever you are having problems in the connection, the best choice will be the OpenVPN with UDP.
IKEv2/IPSec - Compared to an OpenVPN, the IKEv2 is faster in many aspects. This is because IKEv2 in general consumes less amount of CPU resources compared to an OpenVPN. But this cannot be guaranteed in all the cases. There can be different variables which can affect the speed. However for most of the mobile users, IKEv2 will be the best option based on the performance since it does the job of reconnection very well.
L2TP/IPSec - Performance offered by the L2TP can be varying, especially in terms of speed. Due to the fact that the encryption/decryption takes place in the kernel it should boost the overall speed. However since it encapsulates data twice it should be slower compared to other options.
5. Firewall Ports
Open VPN - OpenVPN uses 2 kinds of ports, those are the ports with UDP or TCP. Configuration can be made easily on the OpenVPN so that it can run on either of them. As a result it can bypass restrictive firewalls without an issue.
IKEv2/IPSec - IKEv2 functions using 3 kinds of ports.
Those are the,
UDP 500 - Initial key exchange
IPSec encrypted data (ESP) - Protocol 50
UDP 4500 - NAT traversal
However IKEv2 is made easier to be blocked due to its reliance on ports.
L2TP/IPSec - L2TP works using 3 kinds of ports.
Those are the,
UDP 500 - Initial key exchange
UDP 1701 - Initial L2TP configuration
UDP 4500 - NAT traversal
Similar to the IK2v2, the L2TP can be blocked easily due to its dependence on ports.
一、PPTP
点对点隧道协议 (PPTP) 是由包括微软和3Com等公司组成的PPTP论坛开发的一种点对点隧道协,基于拨号使用的PPP协议使用PAP或CHAP之类的加密算法,或者使用 Microsoft的点对点加密算法MPPE。其通过跨越基于 TCP/IP 的数据网络创建 VPN 实现了从远程客户端到专用企业服务器之间数据的安全传输。

PPTP 支持通过公共网络(例如 Internet)建立按需的、多协议的、虚拟专用网络。PPTP 允许加密 IP 通讯,然后在要跨越公司 IP 网络或公共 IP 网络(如 Internet)发送的 IP 头中对其进行封装。
PPTP协议是点对点隧道协议,其将控制包与数据包分开,控制包采用TCP控制。PPTP使用TCP协议,适合在没有防火墙限制的网络中使用。
二、L2TP
第 2 层隧道协议 (L2TP) 是IETF基于L2F (Cisco的第二层转发协议)开发的PPTP的后续版本。是一种工业标准 Internet 隧道协议,其可以为跨越面向数据包的媒体发送点到点协议(PPP)框架提供封装。PPTP和L2TP都使用PPP协议对数据进行封装,然后添加附加包头用于数据在互联网络上的传输。PPTP只能在两端点间建立单一隧道。

L2TP支持在两端点间使用多隧道,用户可以针对不同的服务质量创建不同的隧道。L2TP可以提供隧道验证,而PPTP则不支持隧道验证。但是当L2TP 或PPTP与IPSEC共同使用时,可以由IPSEC提供隧道验证,不需要在第2层协议上验证隧道使用L2TP。PPTP要求互联网络为IP网络。L2TP只要求隧道媒介提供面向数据包的点对点的连接,L2TP可以在IP(使用UDP),桢中继永久虚拟电路 (PVCs),X.25虚拟电路(VCs)或ATM VCs网络上使用。
L2TP是国际标准隧道协议,它结合了PPTP协议以及第二层转发L2F协议的优点,能以隧道方式使PPP包通过各种网络协议,包括ATM、SONET和帧中继。但是L2TP没有任何加密措施,更多是和IPSec协议结合使用,提供隧道验证。
L2TP使用UDP协议,一般可以穿透防火墙,适合在有防火墙限制、局域网用户,如公司、网吧、学校等场合使用。PPTP和L2TP二个连接类型在性能上差别不大,如果使用PPTP不正常,那就更换为L2TP。
三、IPSec
IPSec隧道模式隧道是封装、路由与解封装的整个过程。隧道将原始数据包隐藏(或封装)在新的数据包内部。该新的数据包可能会有新的寻址与路由信息,从而使其能够通过网络传输。隧道与数据保密性结合使用时,在网络上窃听通讯的人将无法获取原始数据包数据(以及原始的源和目标)。封装的数据包到达目的地后,会删除封 装,原始数据包头用于将数据包路由到最终目的地。

隧道本身是封装数据经过的逻辑数据路径,对原始的源和目的端,隧道是不可见的,而只能看到网络路径中的点对点连接。连接双方并不关心隧道起点和终点之间的任何路由器、交换机、代理服务器或其他安全网关。将隧道和数据保密性结合使用时,可用于提供VPN。
封装的数据包在网络中的隧道内部传输。在此示例中,该网络是 Internet。网关可以是外部 Internet与专用网络间的周界网关。周界网关可以是路由器、防火墙、代理服务器或其他安全网关。另外,在专用网络内部可使用两个网关来保护网络中不信任的通讯。
当以隧道模式使用 IPSec 时,其只为 IP 通讯提供封装。使用 IPSec 隧道模式主要是为了与其他不支持 IPSec 上的 L2TP 或 PPTP VPN 隧道技术的路由器、网关或终端系统之间的相互操作。
四、SSL VPN
SSL协议提供了数据私密性、端点验证、信息完整性等特性。SSL协议由许多子协议组成,其中两个主要的子协议是握手协议和记录协议。握手协议允许 服务器和客户端在应用协议传输第一个数据字节以前,彼此确认,协商一种加密算法和密码钥匙。在数据传输期间,记录协议利用握手协议生成的密钥加密和解密后 来交换的数据。

SSL独立于应用,因此任何一个应用程序都可以享受它的安全性而不必理会执行细节。SSL置身于网络结构体系的 传输层和应用层之间。此外,SSL本身就被几乎所有的Web浏览器支持。这意味着客户端不需要为了支持SSL连接安装额外的软件。这两个特征就是SSL能 应用于VPN的关键点。
典型的SSL VPN应用如OpenVPN,是一个比较好的开源软件。PPTP主要为那些经常外出移动或家庭办公的用户考虑;而OpenVPN主要是针对企业异地两地总分公司之间的VPN不间断按需连接,例如ERP在企业中的应用。
五、OpenVPN产品特点
OpenVPN 允许参与建立VPN的单点使用预设的私钥,第三方证书,或者用户名/密码来进行身份验证。它大量使用了OpenSSL加密库,以及SSLv3/TLSv1 协议。OpenVPN能在Linux、xBSD、Mac OS X与Windows 2000/XP上运行。它并不是一个基于Web的VPN软件,也不与IPsec及其他VPN软件包兼容。
隧道加密
OpenVPN使用OpenSSL库加密数据与控制信息:它使用了OpesSSL的加密以及验证功能,意味着,它能够使用任何OpenSSL支持的算法。它提供了可选的数据包HMAC功能以提高连接的安全性。此外,OpenSSL的硬件加速也能提高它的性能。
OpenVPN提供了多种身份验证方式,用以确认参与连接双方的身份,包括:预享私钥,第三方证书以及用户名/密码组合。预享密钥最为简单,但同时 它只能用于建立点对点的VPN;基于PKI的第三方证书提供了最完善的功能,但是需要额外的精力去维护一个PKI证书体系。OpenVPN2.0后引入了 用户名/口令组合的身份验证方式,它可以省略客户端证书,但是仍有一份服务器证书需要被用作加密.
OpenVPN所有的通信都基于一个单一的IP端口,默认且推荐使用UDP协议通讯,同时TCP也被支持。OpenVPN连接能通过大多数的代理服务器,并且能够在NAT的环境中很好地工作。服务端具有向客户端“推送”某些网络配置信息的功能,这些信息包括:IP地址、路由设置等。OpenVPN提供了两种虚拟网络接口:通用Tun/Tap驱动,通过它们,可以建立三层IP隧道,或者虚拟二层以太网,后者可以传送任何类型的二层以太网络数据。传送的 数据可通过LZO算法压缩。IANA(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority)指定给OpenVPN的官方端口为1194。OpenVPN 2.0以后版本每个进程可以同时管理数个并发的隧道。
OpenVPN使用通用网络协议(TCP与UDP)的特点使它成为IPsec等协议的理想替代,尤其是在ISP(Internet service provider)过滤某些特定VPN协议的情况下。在选择协议时候,需要注意2个加密隧道之间的网络状况,如有高延迟或者丢包较多的情况下,请选择TCP协议作为底层协议,UDP协议由于存在无连接和重传机制,导致要隧道上层的协议进行重传,效率非常低下。
OpenVPN与生俱来便具备了许多安全特性:它在用户空间运行,无须对内核及网络协议栈作修改;初始完毕后以chroot方式运行,放弃root权限;使用mlockall以防止敏感数据交换到磁盘。
OpenVPN通过PKCS#11支持硬件加密标识,如智能卡。
OpenVPN是一个基于SSL加密的纯应用层VPN协议,是SSL VPN的一种,支持UDP与TCP两种方式(说明:UDP和TCP是2种通讯协议,这里通常UDP的效率会比较高,速度也相对较快。所以尽量使用UDP连接方式,实在UDP没法使用的时候,再使用TCP连接方式)。
由于其运行在纯应用层,避免了PPTP和L2TP在某些NAT设备后面不被支持的情况,并且可以绕过一些网络的封锁(通俗点讲,基本上能上网的地方就能用OpenVPN)。OpenVPN客户端软件可以很方便地配合路由表,实现不同线路(如国内和国外)的路由选择,实现一部分IP走VPN,另一部分IP走原网络。
PPTP和L2TP的区别
PPTP和L2TP只是VPN的两种连接方式,只是方式不同,因为每个人的网络环境的差异,需要用适合自己的连接方式,一般首选是PPTP,也有部分使用PPTP不稳定或者无法连接的用户,换L2TP方式连接即可得到很好的解决。
PPTP
点对点点对点隧道协议(PPTP),由微软开发的,与其他技术公司一起,是最广泛支持的Windows客户端的VPN之间的方法。PPTP是一个扩展的互联网标准的点对点点对点协议(PPP),链路层协议,用于在串行链路上传输的IP数据包。PPTP使用相同类型的身份验证的PPP(PAP,SPAP,CHAP,MS-CHAP v.1/v.2和EAP)。
PPTP建立隧道,但不提供加密,PPTP使用微软点对点加密(MPPE)协议来创建一个安全的VPN加密链接。PPTP具有相对较低的开销,这使得它比其他一些VPN方法部署更快。
如何工作:PPTP隧道被实例化的对等通信的TCP端口1723。这个TCP连接,然后用第二GRE(通用路由封装)隧道到同一个发起和管理。
端口/协议: 1723 TCP协议GRE
用户认证协议 EAP-TLS或MS-CHAP v2的
MPPE(微软点对点点对点加密)加密方法:
加密强度: MPPE 40-128位
L2TP
第2层隧道协议(L2TP),思科与微软之间的合作开发的 PPTP的功能结合起来,与思科的专有第2层转发协议(L2F)。
L2TP(第二层隧道协议)支持non-TCP/IP客户和协议(如帧中继,ATM和SONET)。
L2TP不提供任何加密orconfidentiality,本身它依赖于一种加密协议,它通过在隧道内提供保密性。如今L2TP连接 不谈判PPP加密通过使用微软点对点加密(MPPE) 。相反,加密是通过使用Internet协议安全(IPSec)的封装安全负载(ESP)头和尾。同样重要的是要注意,IPsec是比PPTP消耗更多的资源,因此高于PPTP与L2TP溶液的开销。
端口: 1701 UDP
用户认证协议 EAP-TLS或MS-CHAP v2的
*除了提供计算机级身份验证,IPSec提供终端到终端的发送和接收节点之间传递数据的加密。
安全加密:
加密强度: 高级加密标准(AES)256,AES 192,AES 128和3DES加密算法。
L2TP/IPSec和PPTP类似在以下方面:
提供了一个逻辑的传输机制来发送PPP有效载荷。
提供隧道或PPP有效载荷基于任何协议的封装,使得可以通过IP网络发送。
依靠PPP连接过程执行用户认证和协议配置。
有关PPTP的一些特点:
+ PPTP 易于部署
PPTP使用TCP,可靠的解决方案,允许重传丢失的数据包
+支持PPTP
- PPTP的安全性较低,MPPE(最多128位)
-数据加密后开始PPP连接过程(因此,PPP认证)完成
- PPTP连接只需要通过基于PPP的认证协议的用户级身份验证
一些事实over IPSec的L2TP():
+ L2TP/IPSec的数据加密之前就 已经开始PPP连接过程
+ L2TP/IPSec的连接使用三个56位密钥的AES(256位)或DESUup)
+ L2TP/IPSec的连接需要通过计算机级别的认证证书和用户级认证通过PPP认证协议,提供了更强的身份验证
+ L2TP使用UDP。它是一个速度更快,但不太可靠,因为它并没有重新传输丢失的数据包,是常用的实时互联网通信
+ L2TP更多的“防火墙友好”比PPTP -一个关键的优势外联网协议,由于大多数防火墙不支持GRE
- L2TP要求证书签发计算机证书的基础设施
共同点:
PPTP和L2TP都使用PPP协议对数据进行封装,然后添加附加包头用于数据在互联网络上的传输,两个协议非常相似。
不同点:
1、PPTP要求互联网络为IP网络。L2TP只要求隧道媒介提供面向数据包的点对点的连接。L2TP可以在IP(使用UDP),桢中继永久虚拟电路(PVCs),X.25虚拟电路(VCs)或ATM VCs网络上使用。
2、PPTP只能在两端点间建立单一隧道。L2TP支持在两端点间使用多隧道。使用L2TP,用户可以针对不同的服务质量创建不同的隧道。
3、L2TP可以提供包头压缩。当压缩包头时,系统开销(overhead)占用4个字节,而PPTP协议下要占用6个字节。
4、L2TP可以提供隧道验证,而PPTP则不支持隧道验证。但是当L2TP或PPTP与IPSEC共同使用时,可以由IPSEC提供隧道验证,不需要在第2层协议上验证隧道。
使用上的不同:
1、pptp使用简单方便,不需要做额外配置,而l2tp需要共享密钥和修改注册表(对win系列机器讲)。
2、l2tp在穿透方面有时候会比pptp强一些。
3、速度方面两者由于在同一台服务器上,基本没什么差别。
PPTP和L2TP都使用PPP协议对数据进行封装,然后添加附加包头用于数据在互联网络上的传输。尽管两个协议非常相似,但是仍存在以下几方面的不同:
1、PPTP要求互联网络为IP网络。L2TP只要求隧道媒介提供面向数据包的点对点的连接。L2TP可以在IP(使用UDP),桢中继永久虚拟电路(PVCs),X.25虚拟电路(VCs)或ATM VCs网络上使用。
2、PPTP只能在两端点间建立单一隧道。L2TP支持在两端点间使用多隧道。使用L2TP,用户可以针对不同的服务质量创建不同的隧道。
3、L2TP可以提供包头压缩。当压缩包头时,系统开销(overhead)占用4个字节,而PPTP协议下要占用6个字节。
4、L2TP可以提供隧道验证,而PPTP则不支持隧道验证。但是当L2TP或PPTP与IPSEC共同使用时,可以由IPSEC提供隧道验证,不需要在第2层协议上验证隧道。总之,对于一般的使用者来说,L2TP有更强的穿透率,更好的压缩,更好的加密(双层加密),所以如果你在使用PPTP失败的时候可以尝试L2TP。
PPTP、L2TP、OpenVPN三种隧道协议的优缺点对比:
易用性:PPTP > L2TP > OpenVPN
速度:PPTP > OpenVPN UDP > L2TP > OpenVPN TCP
安全性:OpenVPN > L2TP > PPTP
稳定性:OpenVPN > L2TP > PPTP
网络适用性:OpenVPN > PPTP > L2TP
PPTP——最常用,设置最简单,大多数设备都支持
L2TP——支持PPTP的设备基本都支持此种方式,设置略复杂,需要选择L2TP/IPSec PSK方式,且设置预共享密钥PSK
OpenVPN——最稳定,适用于各种网络环境,但需要安装第三方软件和配置文件,较复杂。
PPTP是一个快速、&易于使用协议,具有简单的设置过程。如果您的设备不支持OpenVPN,这是一个不错的选择。
L2TP/IPSec是大多数台式机、手机和平板设备的内建协议。如果您的设备不支持OpenVPN并且安全是重中之重,这是一个不错的选择。IPsec是一项预先安装于大多数台式电脑、手机和平板设备中的协议。我们在指定平台上的IPSec服务支持L2TP和 IKEv2,为您带来快速、安全和可靠的使用体验。
OpenVPN 对于包括Windows, Mac OS X 和 Linux在内的台式机,推荐OpenVPN协议。性能很高——快速,安全,可靠。支持Windows, macOS和Linux等台式电脑操作系统的工业级协议,同时也是一个安全可靠的选择。
WireGuard是最先进、最稳定的VPN协议,它为所有设备提供最快速、最私密和最安全的连接。被认为是VPN协议未来的发展方向。这项灵活的技术由十分简洁的代码架构组成,为您提供最快的速度以及最高级别的隐私性和安全性。
PPTP | L2TP/IPsec | OpenVPN | Wireguard | |
| VPN 加密 | 128 位 | 256 位 |
| 256 位 |
| 应用程序支持 |
|
|
|
|
| 支持手动设置 |
|
|
|
|
| VPN安全 | 基本加密 | 最高加密。检查数据完整性并进行两次数据封装。 | 最高加密。验证带数字证书的数据。通过数字证书对数据进行验证。 | 最高加密。通过数字证书对数据进行验证。最高加密等级,使用最现代的加密密码。 |
| VPN速度 | 由于较低加密而快速 | 需要更多CPU处理以两次压缩数据。设计时充分考虑了对速度和性能的要求,能够提供十分快速、安全和稳定的连接。通常情况下配置过程快捷,无需进行个性化设置。 | 性能最佳的协议。快速,即使等待时间长且在大范围内的连接上。最可靠的VPN协议,提供快速、安全、易于个性化定制的连接。 | 最优性能协议。性能上优于深层数据包检测。即使这高延迟连接且跨越远距离传输时依然保持高速率。最快、性能最佳的协议,所有协议未来的发展方向。使用最优质、最先进的加密方式以保证最安全、最快速的连接。 |
| 稳定性 | 在大部分Wi-Fi热点上工作良好,很稳定。 | 在支持NAT防火墙的设备上表现稳定。 | 最稳定可靠,即使在无线路由器之后,在不稳定的网络上,以及在Wi-Fi热点上。 | 目前仍在测试中。WireGuard®将会被优化,在提供最稳定连接的同时保证速度。 |
| 兼容性 | 在大部分台式机、移动设备、平板操作系统上都有母语。 | 已经预先安装于大多数台式电脑、手机和平板设备的操作系统中。 | 包括Windows, Mac OS X和Linux在内的多种台式电脑操作系统推荐使用的协议,快速、安全且可靠。 | 大多数台式机电脑,Android手机和平板电脑都支持它。 |
| 结论 | PPTP是一项快速、易于使用的协议。如果你的设备不支持 OpenVPN ,它是个好选择。 | L2TP/IPsec 是个绝好的选择,如果 OpenVPN 没有得到你的设备的支持,并且安全是最高因素。 | 对于包括Windows, Mac OS X 和 Linux在内的台式机,推荐OpenVPN协议。性能最高——快速,安全,可靠。 | WireGuard®是一项最新、最快速、最安全的VPN协议。 |
下文为国外友人所总结,原文如下:
| PPTP | IPSec IKEv2 | OpenVPN | WireGuard |
|---|---|---|---|
Intro | |||
| A very basic VPN protocol based on PPP. The PPTP specification does not actually describe encryption or authentication features and relies on the PPP protocol being tunneled to implement security functionality. | IKEv2 (Internet key exchange version 2) is part of the IPSec protocol suite. Standardized in RFC 7296. IPSec has become the defacto standard protocol for secure Internet communications, providing confidentiality, authentication and integrity. | Open-source VPN protocol developed by OpenVPN technologies. Very popular however not based on standards (RFC). Uses a custom security protocol and SSL/TLS for key exchange. Provides full confidentiality, authentication and integrity. | WireGuard® is an extremely fast VPN protocol with very little overhead and state-of-the-art cryptography. It has the potential to offer a simpler, more secure, more efficient, and easier to use VPN over existing technologies. |
Encryption | |||
| The PPP payload is encrypted using Microsoft's Point-to-Point Encryption protocol (MPPE). MPPE implements the RSA RC4 encryption algorithm with a maximum of 128 bit session keys. | IKEv2 implements a large number of cryptographic algorithms including 3DES, AES, Blowfish, Camellia. IVPN implements IKEv2 using AES with 256 bit keys. | OpenVPN uses the OpenSSL library to provide encryption. OpenSSL implements a large number of cryptographic algorithms such as 3DES, AES, RC5, Blowfish. As with IKEv2, IVPN implements AES with 256 bit keys. | Built atop ChaCha20 for symmetric encryption (RFC7539), Curve25519 for Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) anonymous key agreement, BLAKE2s for hashing (RFC7693), SipHash24 for hashtable keys, and HKDF for key derivation (RFC5869). Makes use of a UDP-based handshake and the key exchange uses perfect forward secrecy while avoiding both key-compromise impersonation and replay attacks. |
Security weaknesses | |||
| The Microsoft implementation of PPTP has serious security vulnerabilities. MSCHAP-v2 is vulnerable to dictionary attack and the RC4 algorithm is subject to a bit-flipping attack. Microsoft strongly recommends upgrading to IPSec where confidentiality is a concern. | IPSec has no known major vulnerabilities and is generally considered secure when implemented using a secure encryption algorithm and certificates for authentication. However Leaked NSA presentations indicate that IKE could be exploited in an unknown manner to decrypt IPSec traffic. | OpenVPN has no known major vulnerabilities and is generally considered secure when implemented using a secure encryption algorithm and certificates for authentication. | WireGuard® has no known major vulnerabilities. It is relatively new and has not seen the thorough vetting of OpenVPN, though the code-base is extremely small, so full audits are possible by individuals and not just large organizations. WireGuard® is in-tree with Linux Kernel 5.6 and has been reviewed by a 3rd party auditor. |
Speed | |||
| With RC4 and 128 bit keys, the encryption overhead is least of all protocols making PPTP the fastest. | IPSec with IKEv2 should in theory be the faster than OpenVPN due to user-mode encryption in OpenVPN however it depends on many variables specific to the connection. In most cases it is faster than OpenVPN. | When used in its default UDP mode on a reliable network OpenVPN performs similarly to IKEv2. | WireGuard® benefits from extremely high-speed cryptographic primitives and deep integration with underlying operating system kernel, so speeds are very high with low overhead. Most customers report higher speeds than OpenVPN. |
Firewall ports | |||
| PPTP uses TCP port 1723 and GRE (Protocol 47). PPTP can be easily blocked by restricting the GRE protocol. | IKEv2 uses UDP 500 for the initial key exchange, protocol 50 for the IPSEC encrypted data (ESP) and UDP 4500 for NAT traversal. IKEv2 is easier to block than OpenVPN due to its reliance on fixed protocols and ports. | OpenVPN can be easily configured to run on any port using either UDP or TCP thereby easily bypassing restrictive firewalls. | WireGuard® uses the UDP protocol and can be configured to use any port. May succumb to traffic shaping more easily than OpenVPN due to lack of support for TCP. |
Setup / Configuration | |||
| All versions of Windows and most other operating systems (including mobile) have native support for PPTP. PPTP only requires a username, password and server address making it incredibly simple to setup and configure. | Windows 7+, macOS 10.11+ and most mobile operating systems have native support for IPSec with IKEv2. | OpenVPN is not included in any operating system release and requires the installation of client software. Installation typically takes less than 5 minutes. | WireGuard® is in-tree with Linux Kernel 5.6. Other non-linux operating systems require the installation of a WireGuard® client app. Installation typically takes less than 5 minutes. |
Stability / Compatibility | |||
| PPTP is not as realiable, nor does it recover as quickly as OpenVPN over unstable network connections. Minor compatibility issues with the GRE protocol and some routers. | IPSec is more complex than OpenVPN and can require additional configuration between devices behind NAT routers. However as long as both the server and client support NAT traversal there shouldn't be any issues. | Very stable and fast over wireless, cellular and other non reliable networks where packet loss and congestion is common. OpenVPN has a TCP mode for highly unreliable connections but this mode sacrifices significant performance due to the inefficiency of encapsulating TCP within TCP. | Extremely stable and robust. More stable than OpenVPN when roaming across networks. Uses an initial endpoint for connections and can switch servers while maintaining the connection. Client can also change networks without dropping the connection. |
Verdict | |||
| Due to the major security flaws, there is no good reason to choose PPTP other than device compatibility. If you have a device on which only PPTP is supported then you should consider how to encrypt data at other layers e.g. HTTPS. | IKEv2 is an excellent choice, it is extremely fast, secure and reliable. In addition unlike OpenVPN it requires no additional software to be installed (in most cases) and is therefor the quickest to configure. If you have a threat model that includes sophisticated adversaries then you may want to consider OpenVPN due to the leaked NSA presentations discussed above. | OpenVPN is an excellent choice for all platforms. It is extremely fast, secure and reliable. Additionally, the IVPN Multi-hop network and port forwarding is only available when connecting via OpenVPN. | WireGuard® is an excellent choice and may be the best protocol for high speeds if you don't use the IVPN multi-hop network or port-forwarding. WireGuard® promises better security and faster speeds compared to existing solutions. Since its merge into Linux Kernel (v5.6) and the release of v1.0, we consider WireGuard® to be ready for wide-scale use. |
Supported platforms | |||
|
|
|
|
IPSec Vs OpenVPN
user-space (ovpn) vs. kernel-space (IPsec).
opening 1 udp port (ovpn) on the firewall vs. 2-4 ports (isakmp, esp, ah, nat-t) (IPsec).
TLS on steroids (ovpn) vs. IKE (IPsec) for control.
DIY (ovpn) vs. Vendor & IT support (IPsec).
Easy portability (ovpn) vs. difficult portability because of #1 (IPsec).
Ease of compatability with an external peer (ovpn) vs. various vendor implementations of IPsec.
Both can be tough to implement correctly.
Both have quite the learning curve.
Not so much documentation (ovpn) vs. very extensive documentation (IPsec).
Multicast support (ovpn) vs. GRE trickery (IPsec).
L2 support (ovpn) vs. L2TP trickery (IPsec).
Both are as secure (or insecure) as you make them, as they both support more or less the same ciphers & hashes. However, for IPsec, the supported features are limited by the vendor, which means it is slower to adopt emerging encryption tech (ECC, Quantum Encryption, newer stream ciphers) than OpenVPN.
In this chapter, I will be illustrating IPSec Vs OpenVPN | 5 Differences between IPSec and OpenVPN. For this comparison I will be describing the two versions of IPSec, those are the IKEv2/IPSec and the L2TP/IPSec. Let's get started,
1. Installation
Open VPN - Special client software is needed by the OpenVPN for them to be used. They cannot be incorporated into operating system directly. Therefore, custom OpenVPN apps will be provided by the VPN service providers. These custom OpenVPN apps can be used on most of the operating systems and devices.
IKEv2/IPSec - Installation in IKEv2 is made quick and easy. Only the user has to import the configuration files to the servers IKEv2 is being natively Windows, MacOS, IOS and Android devices. Some operating systems also comes with a function known as the ''always on''. This function ensures that there is no data leaks when the traffic is travelling through the VPN tunnel.
L2TP/IPSec - Same as the IKEv2, a L2TP protocol is fast and easy. And also the user only has to import the configuration files to the servers. Furthermore most Windows, MacOS, Android and IOS devices natively support L2TP.
2. Encryption
Open VPN - OpenSSL and the TLS protocol is used by the OpenVPN to provide encryption. Apart from the it uses different algorithms and ciphers. Some of them are Chacha 20, Blowfish, Camellia and AES. AES encryption used by the OpenVPN is of 160bit/256bit.
IKEv2/IPSec - Algorithm used by the IKEv2 is of cryptographic which includes Blowfish, Camellia, 3DES and AES. AES encryption used by the IKEv2 is of 256bit.
L2TP/IPSec - L2TP in default does not offer any kind of encryption. In L2TP the data those which are arriving from the IPSec protocol will be encrypted twice. The AES encryption used by the L2TP is of 256bit.
3. Security
Open VPN - In terms of security, OpenVPN is far most the best protocol. It does have a proper implementation and very less number of vulnerabilities.
IKEv2/IPSec - IKEv2 protocol is considered to be more secure and reliable. In fact it is one of the popular choices for the VPN users. But one the major drawbacks of it is the closed source.
L2TP/IPSec - Same as the IKEv2, the L2TP is also considered to be secure. But it also has a closed source which is its negative side. However since the L2TP is developed by the cisco and microsoft, it is often questioned about trust.
4. Performance
Open VPN - Regardless of using wireless or cellular networks, an OpenVPN can offer stable and reliable performance. The performance offered by the OpenVPN is generally impressive especially when used along with the User Diagram Protocol (UDP). Therefore, whenever you are having problems in the connection, the best choice will be the OpenVPN with UDP.
IKEv2/IPSec - Compared to an OpenVPN, the IKEv2 is faster in many aspects. This is because IKEv2 in general consumes less amount of CPU resources compared to an OpenVPN. But this cannot be guaranteed in all the cases. There can be different variables which can affect the speed. However for most of the mobile users, IKEv2 will be the best option based on the performance since it does the job of reconnection very well.
L2TP/IPSec - Performance offered by the L2TP can be varying, especially in terms of speed. Due to the fact that the encryption/decryption takes place in the kernel it should boost the overall speed. However since it encapsulates data twice it should be slower compared to other options.
5. Firewall Ports
Open VPN - OpenVPN uses 2 kinds of ports, those are the ports with UDP or TCP. Configuration can be made easily on the OpenVPN so that it can run on either of them. As a result it can bypass restrictive firewalls without an issue.
IKEv2/IPSec - IKEv2 functions using 3 kinds of ports.
Those are the,
UDP 500 - Initial key exchange
IPSec encrypted data (ESP) - Protocol 50
UDP 4500 - NAT traversal
However IKEv2 is made easier to be blocked due to its reliance on ports.
L2TP/IPSec - L2TP works using 3 kinds of ports.
Those are the,
UDP 500 - Initial key exchange
UDP 1701 - Initial L2TP configuration
UDP 4500 - NAT traversal
Similar to the IK2v2, the L2TP can be blocked easily due to its dependence on ports.
该文章最后由 阿炯 于 2021-02-24 11:23:50 更新,目前是第 2 版。
